A few weeks ago, I wrote, “When They Zig, You Should Zag”, about trying to find opportunities hidden in plain site. And with that in mind, I wanted to share this fantastic piece from The Ringer about the unusual lessons that the Atlanta Falcons have learned from a cycling team. It’s a fantastic example of how a team is making small improvements — in the way their players sleep, eat, train, and learn — to get better at their work.
Play The Chorus Another 20 Times.
I write a lot about the work — about the idea that there’s value in putting in the work every day, in trying even when the results aren’t very good, in showing up when you know that you don’t have 100% in you that day.
Here’s what that actually looks like. There’s a story I love from Glenn Frey, formerly of the Eagles, in the documentary “History of the Eagles.” He’s talking about his former downstairs neighbor, Jackson Browne, and the work that Browne used to put into each of his songs:
“We slept late in those days, except around 9 o’clock in the morning, I’d hear Jackson Browne’s teapot going off — this whistle in the distance. And then I’d hear him playing piano.
I didn’t really know how to write songs. I knew I wanted to write songs, but I didn’t know how exactly. You just wait around for inspiration, you know — what was the deal?
Well, I learned through Jackson’s ceiling and my floor exactly how to write songs. Because Jackson would get up, and he’d play the first verse, and the first chorus, and he’d play it 20 times, until he had it just the way he wanted. And then there’d be silence. And then I’d hear the teapot go off again. Then it’d be quiet for 10 or 20 minutes. Then I’d hear him start to play again, and there was the second verse. So then he’d work on the second verse, and he’d play it 20 times. And then he’d go back to the top of the song, and he’d play the first verse, the first chorus, and the second verse another 20 times until he was really comfortable with it, and, you know, change a word here or there. And I’m up there going, ‘So that’s how you do it! Elbow grease, you know, time, thought, persistence.’”
The work doesn’t show up fully formed. You have to do the work over and over again to get it right.
The work will not always be very good. But the work is the only way to get better, and the only way to deliver the results you want.
So go ahead: Play the chorus 20 times, then play it 20 more. Go put in the work.
Try Not To Be Stupid.
I’ve written lovingly about Warren Buffett many times before. (See here, here, here and here.) I’m a fan. And any follower of Buffett’s will tell you that they’re also a fan of his right-hand man, Charlie Munger. Munger has been as important to the rise of Berkshire Hathaway as Buffett himself. And he might be an even better quote than Buffett.
A friend sent me one the other day, from Munger’s 1989 letter to shareholders of the Wesco Financial Corporation. (Berkshire owned them, though Munger served as CEO and Chairman of the board.) In it, Munger dove into the idea of taking risk. He said that taking big risks for short-term gains — particularly by acquiring other companies — is a foolish move:
“Wesco continues to try more to profit from always remembering the obvious than grasping the esoteric. It is remarkable how much long-term advantage people like us have gotten by trying to be consistently not stupid, instead of trying to be very intelligent.”
That’s not to say Munger wouldn’t ever take risks. He wrote:
“Wesco would cheerfully invest $75 million tomorrow, with a 60% chance of total loss, provided the pay-off for winning was large enough to cause statistical expectation to provide a handsome return.”
So what’s the lesson here? Understand who you are and what you do best, and manage risk. It’s okay to bet big sometimes — as long as you understand the size of the opportunity and the amount of risk involved.
Otherwise, Munger’s advice was simple: Try not to be stupid! Yes, he wrote, it’s a strategy that “is bound to encounter periods of dullness.” But it also works in the long-term.
Munger wrote that letter in 1989. Today, he’s worth $1.48 billion. Maybe we should heed his advice.
———
That photo of Munger was taken by Nick Webb, and re-used here thanks to a Creative Commons license.
———
The Rules Don’t Apply.
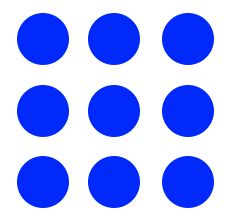
Imagine you’ve got a pencil in your hand, and I give you this challenge: Using four continuous straight lines, without picking up your pencil, what’s the best way to draw a line through every one of those nine dots?
I’ll give you a second.
If you try to go around the outside first before cutting to the middle, that’s five lines. If you try starting in the top left, then going to bottom right, and then up and over and… well, that’s far more than four.
The issue most people have with this puzzle is that they — without even realizing it! — try to stay within the boundaries of the dots. But there’s no rule against going outside the dots. Nobody’s going to stop you from trying something like this:
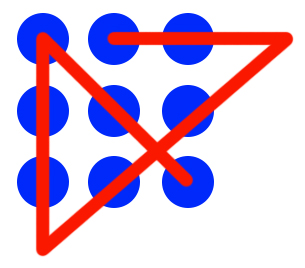
And if there really are no rules[1. Channel your inner Ferris Bueller! Only the meek get pinched!], who’s to say you can’t solve the puzzle with just three lines, like this?
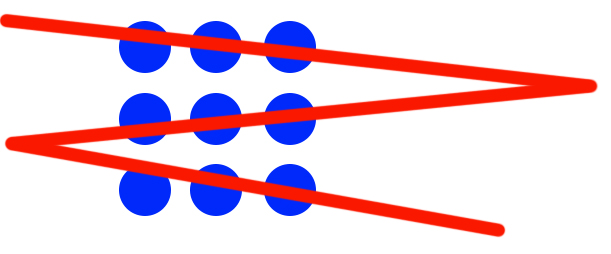
The challenge isn’t in thinking outside the box — it’s thinking entirely without a box! It’s about thinking without any boundaries or rules. Nobody’s going to stop you from trying something unexpected or different. The solutions you’re looking for don’t have to be elegant — they just have to work.
Here’s your permission to break a few rules today. There’s always another way to do the work you want to do.
The 1-1-1 Model.
A friend forwarded me an email the other day — Mikki Halpin’s Action Now newsletter. It’s an email series geared towards inspiring progressive activism, but she said something so wonderful that I wanted to give it a little shoutout here.
Think about all of the things swirling around you, all the opportunities you have to do things and act on your values and choose these three things:
• One thing to be a leader on
• One thing to be a follower on
• One thing to make a habit of
I love this so much. If I had a cubicle wall, I’d print this out and hang it beside my desk. It’s so simple, yet potentially so powerful.
I’ve been trying to think about how to adapt this for my team. Here’s what I’m thinking so far:
One thing to be a leader on — There are always so many projects in the works. Instead of centralizing power among just a handful of leaders, why not spread the responsibility around and give everyone something to take charge on? Even a smaller project — overseeing some design fixes to our newsletters, for instance — could be a great opportunity to give a junior staffer the opportunity to lead.
One thing to be a follower on — As teams gets stretched thin with additional work, it’s easy for a team member to be left alone on a project. And that should never be the case. Everyone should have someone to bounce ideas off of, or to support the work. It’s true that when two people work together on a project, their total output far exceeds what you’d expect from adding 1 + 1 together. Every leader needs a follower to support them.
One thing to make a habit of — Building good habits matter. Whether it’s making time to read in the morning or starting a new routine at the gym, I really believe that building good habits can change your life. And you don’t need to wait for New Year’s Day to resolve to build better habits. You can start today!
That 1-1-1 model — lead, follow, and build good habits — is an amazing example. I can’t wait to bring it to my team.
— — —
That photo of someone to follow comes via Unsplash and photographers Danka & Peter.
Ask, Listen, Learn, Decide. (The Tevye Theory Of Leadership.)
Can we talk about “Fiddler on the Roof” for a second?
I love “Fiddler.” I love the music, and I love the story.[1. I especially love the Lin-Manuel Miranda version of “To Life”, but that’s for another day.] And as I grow into a leadership role at my office, I’ve been thinking a lot about the main character of Tevye, and how his role in “Fiddler” has partly inspired the way I try to make decisions at work.
If you’ve never seen “Fiddler,” here’s the 15-second version: It’s the story of a humble milkman (Tevye), trying to lead his family and his Jewish community through a period of huge upheaval in Russia at the turn of the 20th century. Over the course of the story, Tevye’s homeland rejects him for his religious beliefs; his daughters grow older and marry, but not to the men he’d once envisioned for them; and his family is uprooted from their home. It’s a fascinating — and heartbreaking — story.[2. For Jewish families like mine, watching “Fiddler” can feel like watching a biography of our ancestors.]
Lately, though, I’ve been thinking a lot about Tevye’s role in “Fiddler” story — specifically, the way Tevye adapts to the realignments happening around him. As his world changes, Tevye deals with every new issue by moving through the same four steps:
1) Ask — Tevye asks a lot of questions, seeking to understand the “why” behind changes that affect him.
2) Listen — He listens carefully to what the people he trusts most (his family, his fellow villagers, even some Russian officials) tell him.
3) Learn — He’s receptive to a variety of viewpoints, and willing to accept ideas that aren’t his own. He challenges himself to see things through other people’s eyes.
4) Decide — He tries to make the best decisions he can with the information he’s been given.
And by using the same method for every major change — ask, listen, learn, decide — Tevye consistently makes good decisions. He surrounds himself with people who support him, but who are also willing to challenge him. And Tevye has the humility to understand that by listening to those perspectives, he can push himself towards the best possible decision. In his family, the decisions are always ultimately his, but Tevye never makes a decision without going through that decision-making process first.
All of this matters when you’re making decisions as a leader in your workplace. You have to surround yourself with smart people who are willing to confront you with hard truths. On a team, dissent and disagreement can be a good thing — as long as you’re willing to recognize that you don’t have all the answers. Together, the team can always get to a better solution than you will alone.
The next time you watch “Fiddler,” watch it with Tevye’s process in mind. I think you’ll be impressed at how such a humble character can show such wisdom as a leader.
———
That photo of a “Fiddler” playbill was taken by Deb Nystrom and used here thanks to a Creative Commons license.
Look Up.

I’ve lived in New York City for four years, and in those four years, I don’t believe I’ve ever gone all Tom Friedman and written a post in which I take a tiny public transportation experience and make it into a big thing.
That, sadly, ends today.
So with apologies to the Times’s op-ed page, here’s a story:
I’m riding the subway down to work this morning, and the arrival board on the downtown 6 train has one word on it: “Delay.” I wait for a few minutes, but the subway still hasn’t arrived.
And then a voice comes over the loudspeaker: There’s a sick passenger on the train one stop away, and it’s not moving. If you want to go downtown, please go to the other side of the tracks, take a 6 uptown one stop, and then take an express train back downtown.
It’s annoying. But it is what it is.
So I start walking to the uptown platform, and a handful of people are walking there, too. But everybody else on the platform is just standing there.
The voice comes over again to repeat the message, but most people still aren’t moving.
I get to the other side of the tracks, and I look back at the downtown platform. There must be a hundred people still standing there, completely oblivious to the message from the loudspeaker. I look up and down the platform. Everyone’s in their own world, listening to something via headphones, or loudly locked in conversation with someone else. The trains aren’t moving, and they’re too busy to even notice.
Now here’s where Tom Friedman would make a profound statement about the state of the world based on that one story, and since I’m already this deep into my anecdote, here goes:
We all have ways of building little bubbles for ourselves, and shutting the rest of the world out. You throw on headphones. You hide in our offices, doors closed, or in corners of the building where you won’t be bothered. You tell yourself that you need the quiet, or you need to be productive. You need to get away.
But here’s the downside: That leaves you isolated. You miss out on the things happening all around you — sometimes little, sometimes big and obvious.
I used to laugh about a manager at my office who was infamous for a leadership style called Management By Walking Around. It seemed like such an odd way to lead. But I’m starting to see the benefits. Being visible and keeping your eyes open exposes you to what’s happening around you — at least at the surface level. It opens the door to serendipitous conversations, and as a manager, it’s certainly not a bad thing to be a noticeable presence around the building.
But first you have to open your eyes and ears. Things are happening all around you — it’s up to you to decide if you want to pay them notice.
———
That’s a photo of my subway platform, taken by yours truly.
This Behind-The-Scenes Video Of The ‘SNL’ Crew Tearing Down A Set In Two Minutes Is Absolutely Fascinating.
I love learning about the way other people work — not just what they do during their day, but how they do it. A few years ago, I remember grabbing a burrito at Chipotle late in the afternoon, in the dead time between the lunch rush and dinner. The manager was training a team of new hires how to move customers through the line. The new hires were taking a full minute to get a customer from “Hi, what would you like to order?” to the cashier. The manager wanted them to get it down to 22 seconds. He explained that if there were a dozen people in line, serving a customer in 22 seconds meant that last person in line would be paying for their burrito in a little over 4 minutes. At their current pace, that last customer wouldn’t pay for 12 minutes — and would probably abandon the line for another lunch option long before then.
So I watched as the manager trained each member of the team in ways to shave seconds off of every step of the burrito-making process. The manager kept driving home this message: One person’s work impacts the success of everyone else on the team. It was fascinating to watch.
Which brings me to this video that the “Saturday Night Live” YouTube channel posted a few days ago. Watching the “SNL” crew tear down an entire set in two minutes, it’s impossible not to be impressed by the way everything moves. Four seconds after the actors finish saying, “Live from New York, it’s Saturday Night!”, the crew is already on stage dismantling the set. Then the crew starts dismantling the walls of the set — a set, I should say, that was built specifically to be assembled and dismantled as quickly as possible. And all along, you hear the voice of the director, imploring his team to get the stage clear. We have a family friend who likes to say, “Don’t rush, but hurry up” — and that’s exactly what the director is conveying here.
In less than two minutes, the “SNL” crew manages to make everything on set — the actors, the walls, the fake fireplace, the carpeting — disappear, and those of us watching at home on TV never notice it at all. It’s an impressive bit of teamwork. I don’t know how they move so fast or stay so calm, but they do. I’d watch an entire “SNL” episode just of what happens behind the scenes — I’d love to know more about how their crew trains for the live show. There’s a lot to learn from a team like this.
The One Thing You Can Control Is The Way You Work.
Imagine for a second that you’re a kid again, and you’re fast. You’re really fast. You’re the fastest kid on your block. The fastest guy in your neighborhood. The fastest guy in your school. When you run, everyone else spends a lot of time looking at your backside as you pull away. You don’t run as much as you glide, effortlessly, as though you were born to do this one thing. In a way, you were. For you, running is effortless. You’re the fastest guy in every meet you enter. You’re the fastest kid in the county, the state.
You keep running. You start training with coaches whose whole purpose is to help you find ways to run faster. Your speciality is sprinting, a sport where every hundredth of a second matters. You train to shave .01s off your time. Every fraction of a tick is important. Imagine how many ticks in your life have gone by that you didn’t even notice, and now they all matter. You push every day to find ways to get faster. Your times keep getting better and better. You’re now the fastest guy at your university, the fastest guy at every meet, and those meets are full of runners who were the fastest guy on their street and at their school and in their state — until they ran against you. Imagine that for a second: You were faster than all of them.
One day, you go to a national meet, and you find out that you’re the fastest guy in your entire country. You go to bigger meets, and you win those, too. It’s hard to believe, but the results say it’s true: You’re the fastest guy on the entire continent. Imagine that: the fastest guy out of a billion people! You!
And imagine that you’re so fast that you make it here: To the Olympics. It’s 2008, and you’re in a stadium of tangled steel that the Chinese call the Bird’s Nest. You’re running faster than ever. You’re fast enough to make the quarterfinals of your best race, the 200 meter dash, and then the semis, and then the finals. There are almost 100,000 people in the stands to watch you run for a medal. Imagine: You are one of the eight fastest humans in the world, and now you will run to find out if you are the fastest.
You are not.
You are fourth fastest — still impossibly fast by any definition of the word, but no one seems to care, because the guy one lane over turns out to be the fastest man who ever lived. You are fast, but the guy in lane 5 is a tall Jamaican who runs at speeds that scientists said were unthinkable for humans to reach. He passes you less than five seconds into the turn — nearly impossible in the 200 meter! — and by the time you hit the straightaway, for once, you are looking at someone else’s backside. At the 150 meter mark, you could parallel park an SUV — not some rinky dink little thing, but a Cadillac Escalade — in the gap between him and you.
You still finish fourth in an Olympic final, the fourth fastest human in the world. You’re a quarter of a second away from a bronze, which is damn fast. You’re still the fastest guy on your continent, and an Olympian.
But the Jamaican in lane 5 finishes nearly a full second ahead of you. It’s impossible to imagine, but you try anyway: You are this fast, and yet, there is a human who is that much faster than you. The difference in that one second is the difference between you and sports immortality.
That one second is the difference between you and Usain Bolt.
———
I think about that 200 meter race a lot. I remember watching the finals live from my hotel room in Beijing, and I remember watching Usain Bolt pass the runner in lane 6 within steps. I couldn’t believe it then, and re-watching that race recently, I can’t believe it now. Bolt’s speed is unfathomable.
That runner I asked you to imagine? His name is Brian Dzingai, and he’s from Zimbabwe. He was the only African runner to make the 200 meter finals in Beijing. I like to think about the work he must have put in to make it to the Olympics. It must have taken an astonishing amount of work — physically, mentally, emotionally — to reach those starting blocks. I imagine that journey often, from the fastest kid on his street to one of the fastest men in the world. But I cannot imagine what it must have felt like to realize, after always being the fastest in every meet, to realize that there were humans who were actually faster than you.
I’ve written before about the idea of running your own race in life, and I’ll take the analogy a step further here: What I learned from watching that 200 meter race is that you truly cannot control what happens to the runners beside you. You cannot control how tall they are, or how fast they are. (Bolt was taller by a head, and faster by 0.92 seconds.) You cannot control the resources they have — money, training facilities, coaching. (Bolt surely had the better of all three.)
And you cannot control what you, yourself, are born with.
What you can control is this: The way you work. The hours you work. And the intensity with which you work.
Everyone else is going to run their race. You have to accept that you can only run yours.
When I re-watch that race, I always think about Brian Dzingai, and the work he put in to reach those starting blocks. There’s a man who imagined greatness in himself, and put in the work to be great. You can only control the work you do, and Brian Dzingai did just that. His work got him to the Olympics.
Here’s to you, Brian — and everyone else who puts in the work.
———
That photo was taken by photographer Ross Huggett at the 2012 London Games, and is used here thanks to a Creative Commons license and Flickr.
Being A Sports Fan Made Me An Optimist — Even Though My Teams Always Lose.
I love sports. I love my Washington Capitals and Washington Nationals. I love my Missouri Tigers. I love my Maryland Terrapins.
The only thing is: I happen to root for teams that almost never win the big one.
In my lifetime, my teams have combined for one championship: Maryland’s 2002 national title in basketball.
The rest have a history of coming up a little short. The Caps have been to the Stanley Cup finals only once — but never won a title. The Nats have never won a playoff series in their short history. Missouri basketball is one of the winningest teams to never reach a Final Four. Missouri football has made four conference championships games in the last decade, but lost all four.
For some, watching so many teams come up short might make them pessimists. I’m just the opposite. I’m optimistic because my teams still have yet to raise that big trophy.
Watching those teams has given me such wonderful reminders about the things that make great work happen. To have success, you need great, experienced leaders for your team. You need great team members. And you need to be a little lucky — being in the right place at the right time makes the difference, sometimes.
And I’ve been fascinated by the way my teams handle themselves despite pressure from fans and media. When everyone’s telling them, “No, you can’t,” it’s amazing to watch teams show resilience and unity.
Above all: The championships offer a carrot to keep chasing. There’s is always more work to do. There is always room to get better. There is always time to rewrite your own script.
I don’t know if this year is the year for my teams. But I’m optimistic — as always — that success is within our grasp.
———
That photo of the Maryland football team comes via Flickr user dbking and a Creative Commons license.






